Structure Editor
nmrXiv uses OpenChemLib as its structure editor, which is presented to the user during the submission and, after submission, on the sample level, and on the spectra level within NMRium as, in the Chemical structures section, the user can press + to open the editor. The editor allows drawing up structures from scratch, and it also accepts structures loaded from SMILES. Above the editor, there is a link to this documentation that you can always access by clicking Need help?.
Here we provide an overview of the tools available in the editor:
| Tool image | Usage | Tool image | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Clean canvas: it deletes everything resulting in an empty canvas. |  | Undo: it undoes the last change made. |
 | Tidy up canvas: it changes the coordinates of the molecules and the bonds to provide a better view of the structure in terms of bond lengths and angles. |  | Zoom and Rotate: by clicking anywhere in the space and scrolling up and down, it enables zooming out and in, while scrolling right and left, it rotates clock-wise and counter-clock. |
 | Lasso select: it enables the lasso selection of atoms and bonds to apply bulk actions, such as with the eraser. |  | Mapping: This tool is only for reactions and not applicable in nmrXiv |
 | Stereo configuration unknown: it enables adding question marks on chiral centers with unknown stereo configuration. |  | Enantiomere: this tool extends to three tools: **Abs**, which indicates that the provided enantiomer is the one intended. **Or** indicates that the intended structure is either this one or the other enantiomer. **And** indicates that the intended structure is both this enantiomer and the other one, with equal quantities, which means having a racemic mixture. |
 | Eraser: it deletes atoms and bonds. When applied to atoms, it deletes the adjacent bonds, while when applied to bonds, it only deletes the adjacent atoms having no more bonds. Bulk erasing can be done by selecting a set of atoms and bonds. Please note that erasing a double bond will result in the full deletion and not in reducing the bond to a single one. |  | Text: not applicable in nmrXiv. |
 | When applied in empty space, it draws a bond between two carbon atoms, while when applied on an atom, it draws a bond between that atom and a carbon atom. Additionally, it can link two already existing atoms. It can also increase the bond order (e.g., single bond to double bond). | 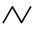 | Chain: it enables drawing saturated aliphatic chains. |
 | Wedge bond: it indicates that the chiral bond is above the ring. It can be used similarly to the bond tool, or to change the bond type. |  | Hatched bond: it indicates that the chiral bond is below the ring. It can be used similarly to the bond tool, or to change the bond type. |
 | Triangle: it enables drawing a triangle of carbons. |  | Square: it enables drawing a square of carbons. |
 | Pentagon: it enables drawing a pentagon of carbons. |  | Hexagon: it enables drawing a hexagon of carbons. |
 | Heptagon: it enables drawing a heptagon of carbons. |  | Benzene: it enables drawing a Benzene molecules. |
 | Charge plus: it increases the positive charge of atoms. |  | Charge minus: it decreases the positive charge of atoms (increases the negative one). |
 | Carbon atom: it creates a carbon atom, along with hydrogen atoms bonded to it, to reach the carbon's four bonds. So if clicked in space, it creates a Methane molecule. It can also replace an existing atom with a carbon one. |  | Silicon atom: it creates a silicon atom, along with hydrogen atoms bonded to it to reach the silicon's four bonds. So if clicked in space, it creates a Silane molecule. It can also replace an existing atom with a silicon one. |
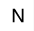 | Nitrogen atom: it creates a nitrogen atom, along with hydrogen atoms bonded to it to reach the nitrogen's three bonds. So if clicked in space, it creates an Ammonia molecule. It can also replace an existing atom with a nitrogen one. |  | Phosphorus atom: it creates a phosphorus atom, along with hydrogen atoms bonded to it to reach the phosphorus' three bonds. So if clicked in space, it creates a Phosphine molecule. It can also replace an existing atom with a phosphorus one. |
 | Oxygen atom: it creates an oxygen atom, along with hydrogen atoms bonded to it to reach the oxygen's two bonds. So if clicked in space, it creates a water molecule. It can also replace an existing atom with an oxygen one. |  | Sulfur atom: it creates a sulfur atom along with hydrogen atoms bonded to it to reach the sulfur's two bonds. So if clicked in space, it creates a Hydrogen sulfide molecule. It can also replace an existing atom with a sulfur one. |
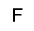 | Fluorine atom: it creates a fluorine atom, along with a hydrogen atom bonded to it, to reach the fluorine's one bond. So if clicked in space, it creates a hydrogen fluoride molecule. It can also replace an existing atom with a fluorine one. |  | Chlorine atom: it creates a chlorine atom, along with a hydrogen atom bonded to it, to reach the chlorine's one bond. So if clicked in space, it creates a hydrogen chloride molecule. It can also replace an existing atom with a chlorine one. |
 | Bromine atom: it creates a bromine atom, along with a hydrogen atom bonded to it to reach the bromine's one bond. So if clicked in space, it creates a hydrogen bromide molecule. It can also replace an existing atom with a bromine one. |  | Iodine atom: it creates an iodine atom, along with a hydrogen atom bonded to it, to reach the iodine one bond. So if clicked in space, it creates a hydrogen iodide molecule. It can also replace an existing atom with an iodine one. |
 | Hydrogen atom: it creates a hydrogen atom, along with a hydrogen atom bonded to it, to reach the hydrogen's one bond. So if clicked in space, it creates a hydrogen molecule. It can also replace an existing atom with a hydrogen one. |  | Atom properties: when applied to an atom, it displays its properties, including the label, mass, valence, and radical state, where the user can edit all of these values. It is mostly useful for isotope and radicals |

